Create a request using the geometries from the map:
- Choose the feature types (hold control button for multiple selection)
- Choose the operation
- Add geometries using the sketching tool (see an example here)
- Alternatively you can insert your own geometry into the field
Select a feature
Resulting URL
Add geometries from map (use sketching tool first)
Geometries:
Result message:
For the analysis functions, the geometries are passed to a REST interface via POST as ESRI-JSON.
In the following section, an overview of parameters will be presented.
In the following section, an overview of parameters will be presented.
Query parameter:
| Parameter | description | mandatory |
|---|---|---|
| spatialtest | The spatial operators are defined in such a way that the operations are mutually exclusive. A geometry can only ever satisfy one spatialtest. Possible values: intersect: Returns all features that are touched by the passed geometries. within: Returns all features in which the passed geometries are completely contained. nearestneighbour : Returns all features that are within a certain distance of the passed geometry (see maxdistancetoneighbour). (Number of returned features can be limited via parameter count). The features are returned in ascending order of distance from the given geometry. valuesatpoint : Returns the values at the given point (currently only applicable to analyse-se feature class hoehe_r). An overview of which featuretypes the different operations are applied to. | mandatory |
| featuretypes | Specifies which analysis object classes are to be taken into account for the analysis. If no analysis object classes are passed, all object classes offered via this rest endpoint will be taken into account. Since the current rest endpoint contains several analysis object classes, this parameter is mandatory. | mandatory |
| count | In combination with the operation (spatialtest) nearestneighbor the maximum number of returned objects can be specified here. Default: 100 | optional |
| maxdistance-toneighbour | In combination with the (spatialtest) nearestneighbor operation, the distance in meters at which neighboring objects are to be returned can be passed here. Default: 100 | optional |
Analyze options:
| Analyze object classes | operation with spatialtest | usage | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| feature type | geometry type | intersect | within | nearestneighbor | valuesatpoint | |
| verw_land_f | vector (polygon) | analyzes federal states and neighbouring states | ||||
| verw_kreis_f | vector (polygon) | analyzes the districts in Saxony | ||||
| verw_gem_f | vector (polygon) | analyzes the municipalities in Saxony | ||||
| kat_gemark_f | vector (polygon) | analyzes the districts in Saxony | ||||
| kat_flurst_f | vector (polygon) | analyzes the parcels in Saxony | ||||
| umw_wassersch_f | vector (polygon) | analyzes water protection areas in Saxony | ||||
| umw_nat2000_f | vector (polygon) | analyzes Fauna-Flora-Habitat areas in Saxony | ||||
| umw_nat2000_p | vector (point) | analyzes bat roosts in Saxony | ||||
| umw_schutzgeb_f | vector (polygon) | analyzes nature reserves in Saxony | ||||
| gesu_aspsz_f | vector (polygon) | analyzes exclusion zones due to findings of african swine fever | ||||
| geol_hohlraumbas_f | vector (polygon) | analyzes cavities in Saxony (underground cavities that are subject to the scope of the Federal Mining Act, areas with mine workings under mining supervision) | ||||
| geol_hohlraumuih_f | vector (polygon) | analyzes cavities in Saxony (areas where underground cavities are to be expected or known) | ||||
| geol_identgebbge_f | vector (polygon) | analyses areas surveyed by the BGE in accordance with the StandAG, which are expected to have favourable geological conditions for the safe disposal of high-level radioactive waste | ||||
| adressen_p | vector (point) | analyzes addresses in Saxony | ||||
| hoehe_r | raster | Contains information on terrain elevation and surface elevation in Saxony | ||||
Thematic overview of available object classes (in German language):
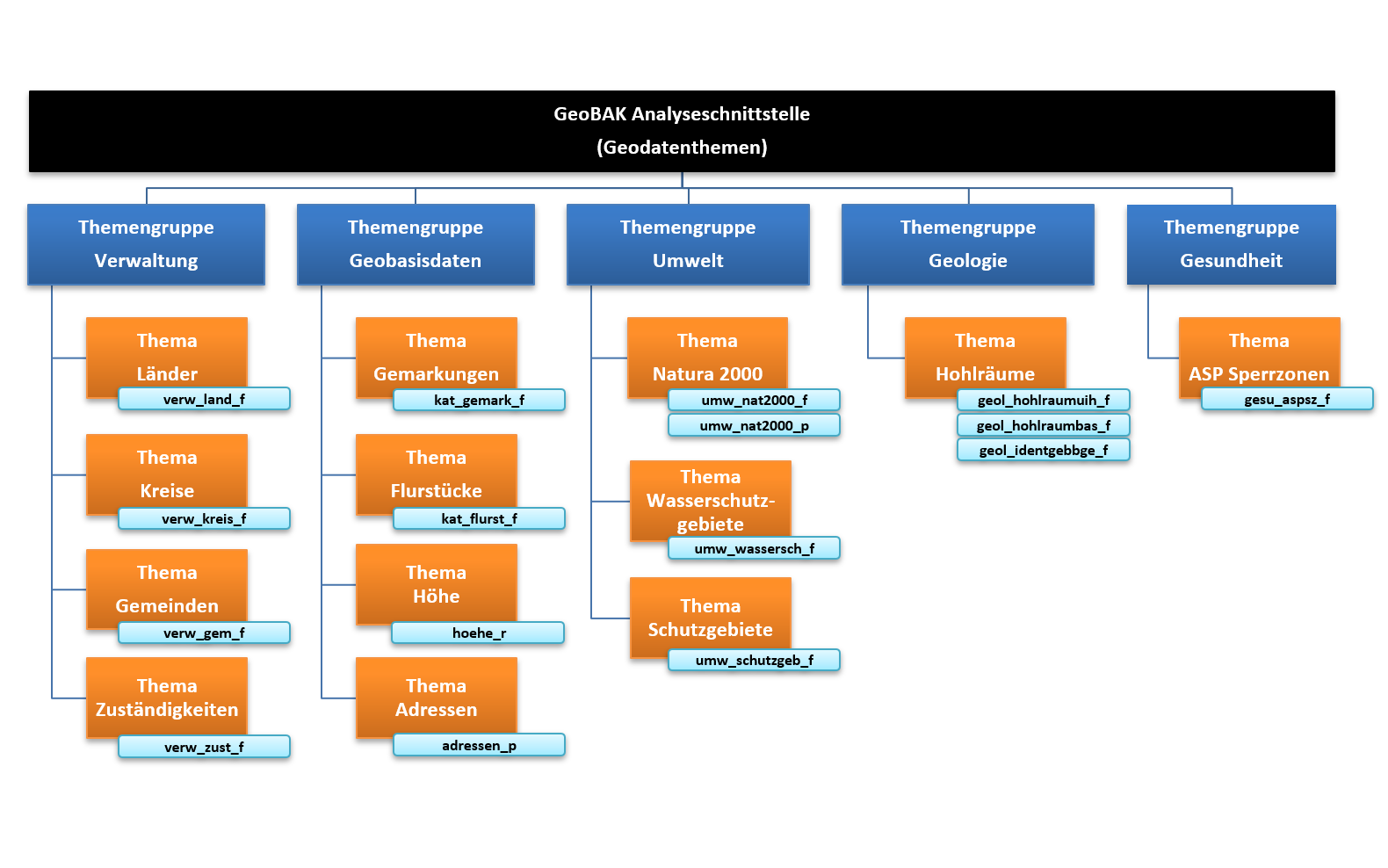

Using the function as seen above, two approaches can be used.
Be aware that you probably need a backend service for sending requests, otherwise you could run into CORS problems.
Custom implementation via native fetch()
- Custom implementation via native fetch()
- IntegrationAPI call
Be aware that you probably need a backend service for sending requests, otherwise you could run into CORS problems.
const url = "https://geodienste.sachsen.de/analyse_tu/guest?featuretypes=kat_flurst_f,kat_gemark_f=&spatialtest=within";
const postParameter =
[
{"geometry":{"x":3863729.06233079,"y":5713497.47625301,"spatialReference":{"wkid":31467}
},"attributes":{}}
,{"geometry":{"x":3864766.61818437,"y":5713404.49919015,"spatialReference":{"wkid":31467}
},"attributes":{}}
,{"geometry":{"x":3864733.54590092,"y":5712696.6991865,"spatialReference":{"wkid":31467}
},"attributes":{}}
];
const response = fetch(url,
{
headers: {
'Accept': 'application/json',
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
method: "POST",
body: JSON.stringify(postParameter)
})
.then( (result) => {
return result.json();
})
.catch(err => {
return err;
});
IntegrationAPI call
function postEvent(functionName, detail) {
const integrationElement = document.getElementById('mapIntegrationElement').contentWindow
if(integrationElement){
integrationElement.postMessage({functionName: functionName, detail: detail}, "*")
}
}
[...]
const parameter = {
url: "https://geodienste.sachsen.de/analyse_tu/guest?featuretypes=kat_flurst_f,kat_gemark_f=&spatialtest=within"
query: [
{"geometry":{"x":3863729.06233079,"y":5713497.47625301,"spatialReference":{"wkid":31467}
},"attributes":{}}
,{"geometry":{"x":3864766.61818437,"y":5713404.49919015,"spatialReference":{"wkid":31467}
},"attributes":{}}
,{"geometry":{"x":3864733.54590092,"y":5712696.6991865,"spatialReference":{"wkid":31467}
},"attributes":{}}
],
timeout: 15000
}
postEvent("analyze",parameter)
window.addEventListener(
"message",
(evt) => {
const functionName = evt.data.functionName
if(!functionName){
return;
}
switch (functionName){
case "analyze": {
response(evt);
break;
}
default:{}
}
},
false
);
